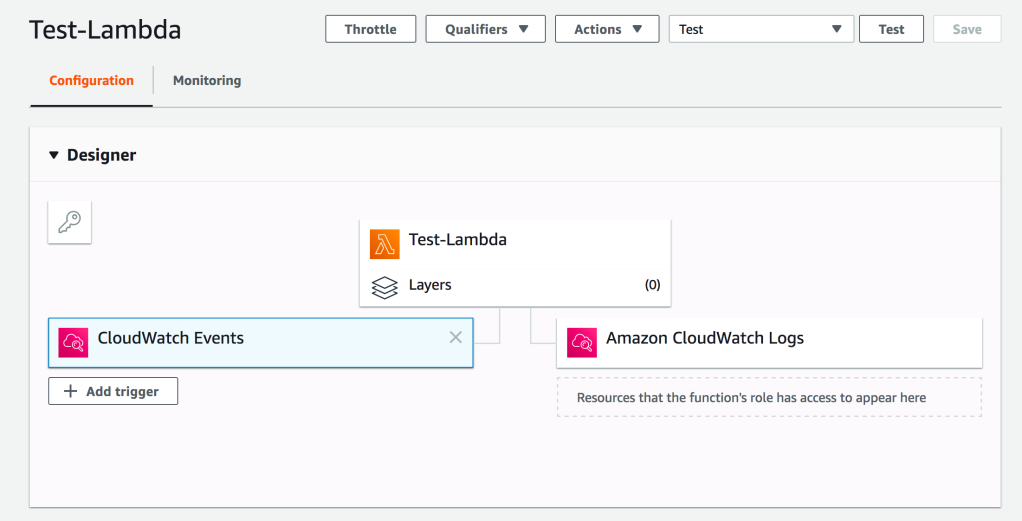
Install latest version of aws-cli
sudo yum remove awscli
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install
/usr/local/bin/aws --versionAdd in Bash Profile path /usr/local/bin
vim ~/.bash_profile
aws --version
aws configure
Create DynamoDB Table
aws dynamodb create-table \
--table-name CustomerRecords \
--attribute-definitions \
AttributeName=CustomerID,AttributeType=S \
AttributeName=RecordDate,AttributeType=S \
--key-schema \
AttributeName=CustomerID,KeyType=HASH \
AttributeName=RecordDate,KeyType=RANGE \
--billing-mode PAY_PER_REQUEST
# Delete DynamoDB Tableaws dynamodb delete-table --table-name CustomerRecords
# Enable Point-in-Time-Recoveryaws dynamodb update-continuous-backups --table-name CustomerRecords --point-in-time-recovery-specification PointInTimeRecoveryEnabled=TrueLoad Records
import boto3
import faker
import sys
# Generate fake data
def generate_data(size):
fake = faker.Faker()
records = []
for _ in range(size):
record = {
'CustomerID': fake.uuid4(),
'RecordDate': fake.date(),
'Name': fake.name(),
'Age': fake.random_int(min=0, max=100),
'Gender': fake.random_element(elements=('Male', 'Female', 'Other')),
'Address': fake.sentence(),
'Description': fake.sentence(),
'OrderID': fake.uuid4()
}
records.append(record)
return records
def write_data_in_chunks(table_name, data, chunk_size):
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
for i in range(0, len(data), chunk_size):
with table.batch_writer() as batch:
for record in data[i:i+chunk_size]:
batch.put_item(Item=record)
print(f"Successfully wrote {len(data)} records to {table_name} in chunks of {chunk_size}.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
table_name = 'CustomerRecords'
chunk_size = int(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 1000
data = generate_data(chunk_size)
write_data_in_chunks(table_name, data, chunk_size)$ python3 load_to_dynamodb.py 1000Calculate Unix Epoch time in milliseconds
date +%s
1710374718Full export
aws dynamodb export-table-to-point-in-time \
--table-arn arn:aws:dynamodb:ap-southeast-2:11111111:table/CustomerRecords \
--s3-bucket customerrecords-dynamodb \
--s3-prefix exports/ \
--s3-sse-algorithm AES256
--export-time 1710374718Incremental export, starting at the end time of the full export
aws dynamodb export-table-to-point-in-time \
--table-arn arn:aws:dynamodb:ap-southeast-2:11111111:table/CustomerRecords \
--s3-bucket customerrecords-dynamodb \
--s3-prefix exports_incremental/ \
--incremental-export-specification ExportFromTime=1710374718,ExportToTime=1710375760,ExportViewType=NEW_IMAGE \
--export-type INCREMENTAL_EXPORTImportant Note :
- ExportFromTime here is the finish time of the Full export and ExportToTime is the current datetime calculated using date +%s command
- Difference between export period from time and export period cannot be less than 15 minutes